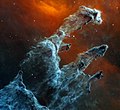
Файл:Pillars of creation - JWST, MIRI - STScI-01GFRYYRTCTMX197BY86MBFCR9.png

Размер этого предпросмотра: 656 × 600 пкс. Другие разрешения: 263 × 240 пкс | 525 × 480 пкс | 840 × 768 пкс | 1120 × 1024 пкс | 1987 × 1817 пкс.
Исходный файл (1987 × 1817 пкс, размер файла: 4,06 Мб, MIME-тип: image/png)
История файла
Нажмите на дату/время, чтобы посмотреть файл, который был загружен в тот момент.
| Дата/время | Миниатюра | Размеры | Участник | Примечание | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| текущий | 21:06, 29 октября 2022 |  | 1987 × 1817 (4,06 Мб) | Fabian RRRR | Uploaded a work by Credits: SCIENCE: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI IMAGE PROCESSING: Joseph DePasquale (STScI), Alyssa Pagan (STScI) from https://webbtelescope.org/contents/media/images/2022/053/01GFRYSFM89AFADVAA0W625BSB with UploadWizard |
Использование файла
Следующие 2 страницы используют этот файл:
Глобальное использование файла
Данный файл используется в следующих вики:
- Использование в da.wikipedia.org
- Использование в de.wikipedia.org
- Использование в en.wikipedia.org
- Использование в es.wikipedia.org
- Использование в fr.wikipedia.org
- Discussion utilisateur:O. Morand
- Discussion utilisateur:Padawane
- Discussion utilisateur:L'amateur d'aéroplanes
- Discussion utilisateur:Sammyday
- Discussion utilisateur:Oziris
- Discussion utilisateur:Pautard
- Discussion utilisateur:Ghoster
- Discussion utilisateur:Hadrianus
- Discussion utilisateur:GabrieL
- Discussion utilisateur:Borvan53
- Discussion utilisateur:Theoliane
- Discussion utilisateur:Abalg
- Discussion utilisateur:Michel421
- Discussion utilisateur:Kimdime
- Discussion utilisateur:Cantons-de-l'Est
- Discussion utilisateur:A1AA1A
- Discussion utilisateur:Hégésippe Cormier
- Discussion utilisateur:Erik Bovin
- Discussion utilisatrice:Manacore
- Discussion utilisatrice:Gráinne Ni Mháille
- Discussion utilisateur:K.A
- Discussion utilisateur:Skimel
- Discussion utilisateur:ContributorQ
- Discussion utilisateur:Mandariine
- Discussion utilisateur:HMa
- Discussion utilisateur:Bertrouf
- Discussion utilisateur:O-R/Archive
- Discussion utilisateur:Lagribouille
- Discussion utilisateur:Jean-Paul Corlin
- Discussion utilisateur:Tylwyth Eldar
- Discussion utilisateur:Starus
- Discussion utilisateur:Sunrise156
- Discussion utilisateur:O.Taris
- Discussion utilisateur:Ælfgar/6649
- Discussion utilisateur:Sernin seb-calmetaf
- Discussion utilisateur:Bounè rodzo
- Discussion utilisateur:Goodshort
- Discussion utilisateur:Polmars
- Discussion utilisateur:BerwaldBis
- Discussion utilisateur:GrandCelinien
- Discussion utilisateur:Olivier Tanguy
- Discussion utilisateur:Jack Rabbit Slim's
- Discussion utilisateur:Io Herodotus/Archive 2021-2023
- Discussion utilisateur:Julien1978/Archive 7
- Discussion utilisatrice:Esprit Fugace/Archive22
- Discussion utilisateur:Harrieta171/1
Просмотреть глобальное использование этого файла.